
Supply Chain Management and Logistics: A Complete Business Guide
Yet many businesses still confuse supply chain management with logistics management—or treat them as isolated functions. This complete guide explains supply chain management and logistics, real-world processes, key differences, and why modern businesses need digital tools.
What Is Supply Chain Management and Logistics? A Complete Guide for Businesses
In today’s fast-moving business environment, products don’t win customers—delivery speed, accuracy, and reliability do. Whether you’re a manufacturer, distributor, retailer, or a growing logistics company, understanding supply chain management and logistics is no longer optional. It is the backbone of profitable, scalable operations.
Yet many businesses still confuse supply chain management with logistics management—or treat them as isolated functions. In reality, they work together to ensure goods move seamlessly from raw material suppliers to end customers.
This guide breaks down supply chain management and logistics in a simple, practical way, connects theory to real-world operations, and explains why modern digital tools are becoming essential.
Understanding Supply Chain Management and Logistics
At a high level, supply chain management and logistics refer to the planning, execution, and optimization of how goods, information, and finances move across an entire business ecosystem.
What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) focuses on the end-to-end coordination of activities involved in producing and delivering a product.
It includes:
Sourcing raw materials
Managing suppliers and vendors
Production planning
Inventory control
Demand forecasting
Distribution strategy
SCM is strategic in nature. It answers questions like:
Where should inventory be stocked?
How much should we produce?
Which suppliers reduce long-term risk?
What Is Logistics Management?
Logistics management is a subset of SCM and deals with the physical movement and storage of goods.
It includes:
Transportation planning
Warehousing and storage
Order fulfilment
Packaging and handling
Last-mile delivery
Returns and reverse logistics
Logistics management is operational. It focuses on how fast, how accurately, and how cost-effectively goods move.
How Supply Chain and Logistics Work Together
Think of supply chain management as the brain and logistics management as the muscle.
SCM designs the strategy
Logistics executes it on the ground
Without logistics, supply chain plans remain theoretical.
Without supply chain planning, logistics becomes reactive and expensive.
That’s why modern businesses integrate logistics management and supply chain management into a single operational framework.
Key Components of Supply Chain Logistics Management
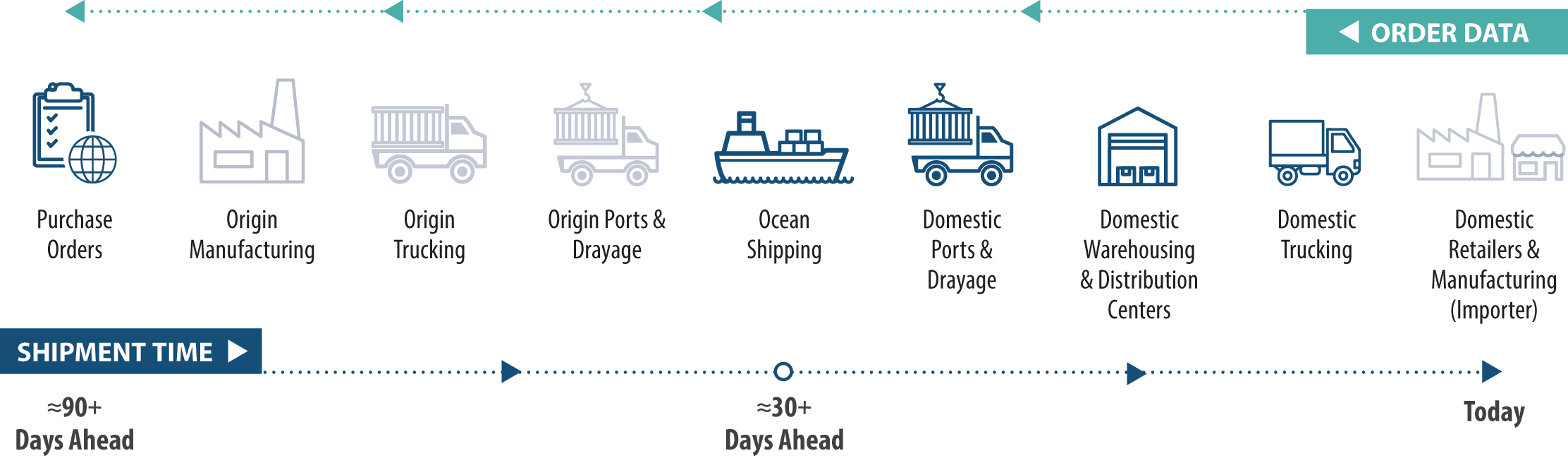
1. Procurement and Supplier Management
This stage ensures raw materials and goods are sourced at the right cost, quality, and timeline. Poor supplier coordination leads to delays, shortages, and excess inventory.
2. Inventory and Warehouse Management
Inventory decisions directly impact cash flow. Overstocking increases holding costs, while understocking results in missed sales.
Modern logistics management relies on:
Real-time stock visibility
Demand-based replenishment
Multi-warehouse coordination
3. Transportation and Freight Movement
Transportation is often the highest cost component of logistics.
This includes:
Route optimization
Carrier selection
Freight rate management
Multimodal transport (road, rail, sea, air)
4. Order Fulfilment and Delivery
Customers judge businesses by delivery accuracy and speed. Order fulfilment involves picking, packing, dispatching, and final delivery coordination.
5. Returns and Reverse Logistics
Returns are no longer an exception. Efficient reverse logistics improves customer trust and recovers value from returned goods.
Supply Chain Management vs Logistics Management (Comparison)
Aspect | Supply Chain Management | Logistics Management |
|---|---|---|
Scope | End-to-end strategy | Execution-focused |
Focus | Planning & coordination | Movement & storage |
Time Horizon | Long-term | Short-term |
Includes | Suppliers, production, demand | Transport, warehouse, delivery |
Business Impact | Cost optimization & resilience | Speed & service quality |
This distinction helps businesses invest correctly—strategy first, execution second.
Real-World Challenges Businesses Face Today
Despite awareness, many companies still struggle with supply chain logistics management due to:
Manual processes and spreadsheets
Lack of real-time shipment visibility
Poor coordination between teams
Inaccurate demand forecasting
Fragmented systems across vendors
As businesses scale, these problems multiply, leading to:
Missed delivery timelines
Rising logistics costs
Customer dissatisfaction
Why Digital Tools Are Now Essential
Traditional supply chain setups relied on phone calls, emails, and Excel sheets. While workable at small volumes, they collapse under scale.
Modern logistics management platforms enable:
Centralized shipment tracking
Automated documentation
Smart alerts and exception handling
Data-driven decision making
Businesses adopting digital supply chain tools gain:
Faster turnaround times
Lower operational costs
Better compliance
Higher customer retention
This is why companies are rapidly moving toward cloud-based supply chain management solutions.
How Businesses Can Strengthen Their Supply Chain
To improve supply chain management and logistics, businesses should focus on:
Process standardization
Visibility across suppliers and transport partners
Automation of repetitive tasks
Data analytics for forecasting and optimization
Technology integration across departments
FAQs: Supply Chain Management and Logistics
1. Is logistics the same as supply chain management?
No. Logistics is a part of supply chain management. SCM is broader and includes planning, sourcing, and coordination, while logistics focuses on movement and storage.
2. Why is supply chain management important for businesses?
It helps reduce costs, improve delivery timelines, manage risk, and scale operations efficiently.
3. Can small businesses benefit from supply chain management?
Absolutely. Even SMEs benefit from better inventory planning, supplier coordination, and logistics visibility.
4. How does technology improve logistics management?
Technology provides real-time tracking, automation, analytics, and better coordination between teams and partners.
Final Thoughts
Understanding supply chain management and logistics is the first step toward building efficient, resilient, and scalable operations. Businesses that treat logistics as a strategic function—not just a cost centre—gain a lasting competitive advantage.
As markets grow more complex, the winners will be those who invest early in structured supply chain planning and modern logistics management systems.
Let’s Move Your Business Forward.
Fast, reliable, and customized logistics solutions at your fingertips.